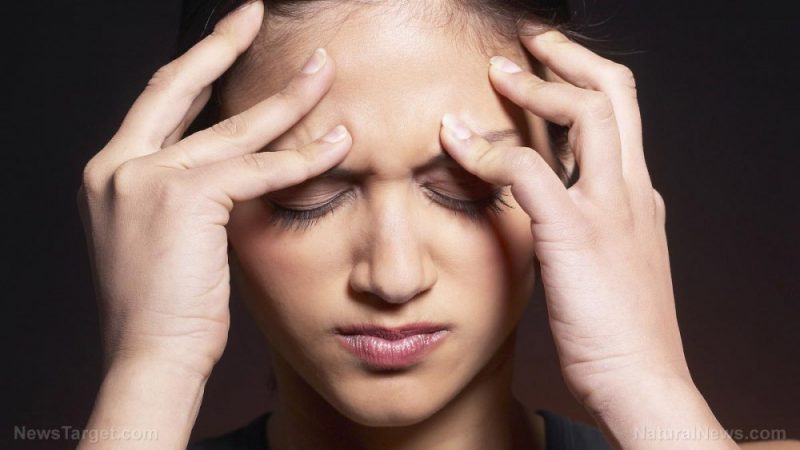
In this study, Iranian researchers examined the impact of self-administered acupressure on sleep quality and fatigue among patients with migraine. Their results were published in the journal Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.
- Poor sleep quality and fatigue are two of the most common complaints associated with migraine. These problems contribute to the development of severe headaches.
- This double-blind, randomized controlled trial involved 76 patients from the neurology clinic of Valiasr (PBUH) teaching hospital, all of whom suffered from migraine without aura.
- The researchers randomly assigned these patients to either an acupressure group or a sham acupressure group.
- They used a demographic questionnaire, the Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index and the Fatigue Severity Scale to collect data from the patients.
- Both groups were trained for four consecutive weeks to apply acupressure on acupoints and sham points, respectively, three times weekly at bedtime.
- The researchers analyzed the data using Chi-square, independent-sample t, paired-sample t and ANCOVA tests at the significance level of less than 0.05.
- After controlling sleep quality mean scores at baseline, the researchers found no significant difference between the sleep quality of the two groups after intervention.
- On the other hand, the mean scores for fatigue significantly decreased in both the acupressure and sham acupressure groups.
- The decrease in the acupressure group was significantly greater than the decrease in the sham acupressure group.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that acupressure is a non-invasive and non-pharmacological therapy that can significantly reduce fatigue in patients with migraine.
Journal Reference:
Vagharseyyedin SA, Salmabadi M, Bahramitaghanaki H, Riyasi H. THE IMPACT OF SELF-ADMINISTERED ACUPRESSURE ON SLEEP QUALITY AND FATIGUE AMONG PATIENTS WITH MIGRAINE: A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice. May 2019;35:374–380. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2018.10.011